Answering questions: How many types of vitamins are there? What is the function of vitamins?
Vitamins are known as one of the most important micronutrients involved in cell structure, metabolism and energy supply of the body. However, did you know that: Our body cannot synthesize vitamins by itself but must mostly get them from outside food. The role and function of vitamins in general, we all know. But with each type of vitamin, their effects on the body are relatively different.
In this article, let's find out with NanoFrance what types of vitamins there are and what specific effects of vitamins are? Don't forget to check it out!
I. How many types of vitamins are there? – Do you know?
There are currently 13 types of Vitamins: Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K and B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, vitamin B6, vitamin B12 and folate). They are divided into 2 main types:
Fat-soluble vitamins
The group of fat-soluble vitamins includes: vitamin D, vitamin A, vitamin E and vitamin K. This type of vitamin is absorbed into the body through fatty tissues and fat. Therefore, if the body cannot absorb fat, it will lack these vitamins. In the process of absorbing them, acid is needed as an emulsifier because fat does not dissolve in the blood.
These vitamins play an important role in protecting vision, developing bones, supporting blood clotting and even preventing cancer.

Water-soluble vitamins
Similar to fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble vitamins can dissolve in water. This also means that they are quickly absorbed into the body. A notable feature of this group of vitamins is that the body cannot store them. In other words, if the amount of vitamins taken in is too large, the body cannot absorb it all, and the excess vitamins will be excreted through urine.
Water-soluble vitamins include: vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin C, vitamin B12, etc. (Vitamin C and group B).
So what is the specific function of each type of Vitamin? The following part of this article will give you the answer. Don't forget to refer to it!
II. What are the functions of Vitamins? What effects do they have on the body?
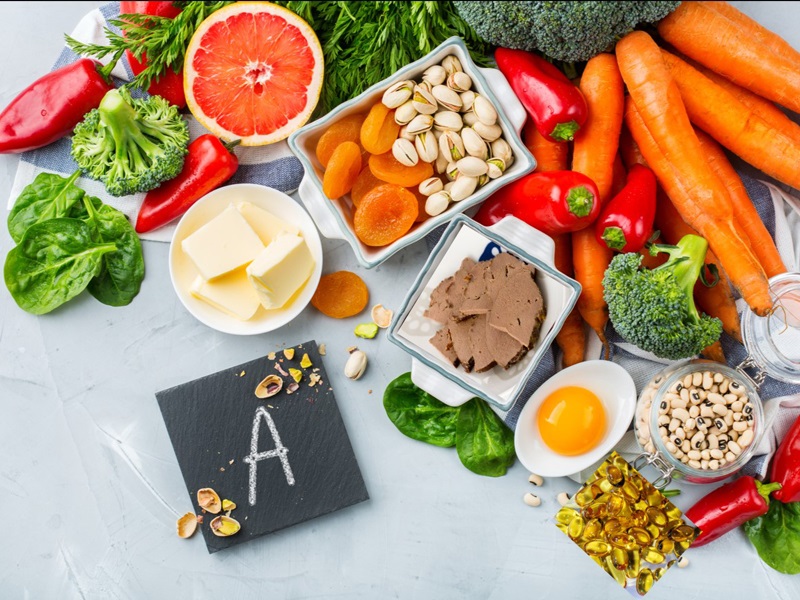
1. What is the function of Vitamin A?
This vitamin plays an important role in many processes and reactions in the body such as:
- Redox Process
- Structure of the photoreceptor regulator in the eye – rhodopsin
- Role and function of epithelial tissues
…
In fact, a lack of Vitamin A will lead to infections, degeneration, infections, vision problems... Vitamin A is abundant in vegetables, fruits, oils, fats...
The recommended amount of Vitamin A for adults is 5,000 IU/day.

2. Effects of B vitamins on the body
For B vitamins, the role of each type is as follows:
Function of Vitamin B1
Vitamin B1 participates in the body's important carbohydrate metabolism. Deficiency of this nutrient will cause many metabolic disorders such as: pyruvic acid accumulation in the blood, nerve impulse conduction disorders, heart activity disorders, etc. They are abundant in egg yolks, liver, milk, bran, etc. and are synthesized by some intestinal bacteria.

What is the role of vitamin B2?
They are components of many enzymes in the body, related to hair loss, oral mucosal damage, eyelid ulcers, etc. You can supplement Vitamin B2 into your body through foods such as milk, liver, yeast, green vegetables, cereals, etc.

Function of Vitamin B3 for the body
This is an important component for coenzyme synthesis, participating in many oxidation-reduction processes, related to neurological disorders, skin and mouth ulcers, body fatigue, general weakness, etc. Foods such as vegetables, fish, meat, milk, liver, etc. are rich in Vitamin B3.
What do you know about the effects of Vitamin B6?
This vitamin can help the body reduce the risk of heart disease. In addition, it helps convert food into energy and helps the body fight infections. Pregnant and breastfeeding women need enough vitamin B6 to help the baby's brain develop.
Some foods such as bananas, beans, carrots, cheese, chicken, lentils, brown rice, tuna, sunflower seeds, whole grain flour... are rich in Vitamin B6.

What role does vitamin B9 play?
Also known as folic acid or folic. This vitamin helps in growth and development of the body. Vitamin B9 matures red blood cells through the synthesis of purine, pyrimidines, and it also participates in the development of methionine of the fetal nervous system.
Experts also recommend eating lots of dark green leafy vegetables, cereals, bread, nuts and beans... to supplement Vitamin B9 for the body.

Vitamin B12 and its important role in the body
One of the most prominent functions of Vitamin B12: Preventing anemia. They help blood cells and nerve cells stay healthy. In particular, they also participate in repairing and regenerating peripheral nerves. The best natural sources of Vitamin B12: meat, nutritional yeast, cereals.

3. The role of Vitamin C
This type of vitamin participates in many metabolic processes in the body, acting as a hydrogen transporter. In addition, it also helps maintain cell activity in tooth, cartilage, bone tissues, etc. A deficiency of vitamin C in the body will cause disorders such as bleeding gums, more severe cases can cause internal bleeding, etc.
Vitamin C is found in many fresh fruits and green vegetables such as guava, orange, lemon, kiwi...
Average dose needed to supplement the body: 80-100mg/day.

4. What is the role of vitamin D?
They play an extremely important role in the absorption of Calcium and Phosphorus in the intestines, synthesizing and strengthening bones. People who do not supplement enough Vitamin D for their bodies often have diseases such as rickets, osteoporosis, soft bones, etc. Vitamin D is abundant in fish liver, egg yolks, butter, fat, etc.
Recommended Vitamin D intake is about 400IU/day.
5. Revealing the function of Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that helps regulate reproduction. If the body does not have enough vitamin E, it will cause degeneration of the reproductive organs, affecting the embryogenesis process, related to the synthesis of red blood cells and blood. You can supplement this vitamin by eating a lot of lettuce, egg yolks, fat, etc.
Recommended Vitamin E intake is about 10-30mg/day.

6. Discover the amazing functions of Vitamin K
Did you know that Vitamin K plays an important role in blood clotting, so a deficiency of this nutrient often causes subcutaneous bleeding, difficulty in blood clotting, etc.
Recommended dosage: 10-15mg/day (for children) and 1mg (for adults).
Hopefully, with the above information, it has helped you understand more about the function of Vitamins and their effects on the body. Try to balance them in your family's daily menu. Don't forget to regularly follow the NanoFrance Website to update more knowledge about the latest medicine and pharmacy!









